Updated: 04/01/2024
A Business Owner’s Guide to Dedicated Internet Access
Your enterprise operations need reliable business Internet connectivity that guarantees access to your data and critical business applications whenever you need them. Many APX Net customers turn to our Dedicated Internet Access Solutions (DIA) to provide the low latency, always-on connection they need.
But not all dedicated Internet connections are the same. Your business needs to understand the differences in:
- Types of circuits
- Reliability
- Speed
- Service levels
- Support
What is Dedicated Internet Access?
Dedicated Internet Access, or DIA, is an internet connection that is completely dedicated to your business. Dedicated Internet Access services provide your business with a private, one-to-one connection between your business and your Internet service provider (ISP). The connection is not shared by other neighboring businesses, which ensures a high connection quality with less latency and jitter compared to shared connections. Plus, DIA provides enterprise-level, carrier-grade features and high speeds.
DIA is particularly beneficial to businesses that need constant access to cloud applications or often stream videos or webinars. Any communication – whether it be high-volume emails, instant messages or video conferencing – is enhanced by the speed and capacity of DIA. The dedicated bandwidth also makes transferring and sharing files easier— especially if those files are typically very large (like in a creative organization like a marketing agency, architecture firm or engineering practice).
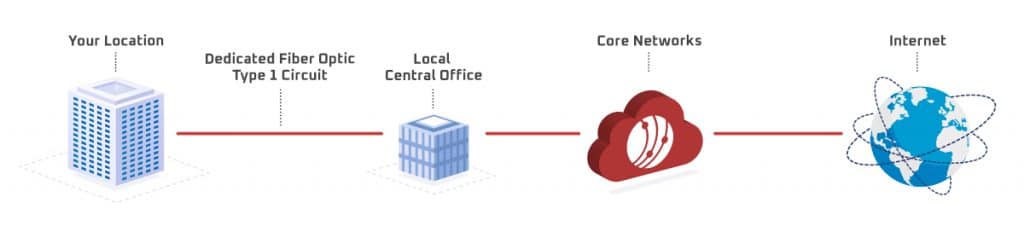
How Does Dedicated Internet Access Work?
DIA works through a circuit, which is the cabling that carries internet services to businesses. Circuits are physical, wired paths that internet connections travel through every time you upload or download data. Let’s break down the different technologies that DIA uses to deliver service and the types of circuits you need to know about:
DIA Technology
DIA circuits use one of several technologies, including Ethernet over Fiber, Ethernet over Copper (EoC), T1 (DS1), T3 (DS3), or fixed wireless. With technologies that use the copper network like EoC, T1, or T3 network availability decreases as the distance increases. Fiber, which is not impacted by distance is the best option if it’s available at your location since it offers consistent speeds. Ethernet over Fiber also scales easily from 10Mbps all the way up to 100Gbps.
DIA Circuit Type I vs Type II
The type of circuit – Type I or II – also makes a difference with installation, latency, service levels, and support.
Type I circuits are connections for which the last mile network provider and the Internet Service Provider (ISP) are the same. With one network and less network hops you can expect shorter installation times, less latency during data transfer, and faster repair times.

Type II circuits are connections for which the last-mile provider and the ISP are different. Multiple providers introduce points of failure along the way as internet traffic travels from network to network. Type II circuits have higher latency due to the cross-connections and greater distance packets need to travel. Multiple providers also result in lower support levels since they often pass off responsibility and blame when service disruptions occur.

Learn More About Type 1 Circuits https://vimeo.com/864471895
Benefits of Dedicated Internet Access
DIA provides several tangible benefits to your business internet and data network connection needs, including:
Reliability
Depending on the technology and circuit type used for DIA, the level of reliability can vary widely. Be sure to check the provider’s service level agreement (SLA) for guaranteed performance levels and uptime. Keep in mind that if your provider offers 99.9 percent uptime, you should expect more than 8 hours of downtime during the year. Can you afford to be down for an entire day? If not, look for five 9s (99.999 percent), which is only 5 minutes for the year.
Low Latency
DIA technology and circuit type can also impact latency, or the delay before data transfer begins. High latency results in poor performance for critical applications like real-time video, financial transactions, or data replications. Type I circuits that travel a single network have less latency as do those using fiber, which transmits data using light (photons) instead of electrons and does not require the signal to be repeated as frequently.
Scalability
DIA technology varies in scalability, which may not seem important when you’re small, but if you’re growing or your traffic fluctuates widely (think seasonal retail needs), then it’s vital. Many technologies top out quickly; DS3, for example, is only good up to 45Mbps. Then you must buy another DS3 whether you need that much bandwidth or not. Ethernet over fiber is ideal for scalability, enabling you to easily grow your bandwidth incrementally from 10Mbps to 100Gbps.
Support
As mentioned, Type I circuits are delivered by one provider, so getting support without the finger-pointing possible with Type II circuits involving multiple carriers is an immediate advantage. Additionally, you’ll want to look for a provider that has an engineering team that will work with you from end-to-end – from determining your bandwidth requirements to managing the implementation process and resolving service issues around the clock.
Productivity
When working in offices, warehouses, hotels or other facilities, a high-quality internet connection can often be the key to whether your employees can function and get their work done or be stalled for hours trying to troubleshoot bad connections. All that added up time can amount to thousands of dollars in payroll, if not hundreds of thousands, if your organization is a nationwide enterprise.
Is Dedicated Internet Access Right for Your Business?
Before deciding on whether DIA is right for your business, you should consider other types of internet connections, your bandwidth needs, your business requirements and the costs.
What are Your Bandwidth Needs?
Multiple factors can affect network performance, but one of the most significant is network bandwidth. Bandwidth measures how much data can pass through the network in a fixed period. The more devices connected to your network actively using the Internet means that more bandwidth is required to access the data on each device at any given moment.
But how do you determine how much bandwidth you need? You need to determine the following factors:
- How many employees do you have?
- How many active workstations and connected devices do you have?
- Which applications are running on the connected network devices?
Need help determining your bandwidth? Contact APX Net for a free consultation.
What Types of Business Internet Connections are Available for Your Business?
DIA isn’t the only type of connection available to businesses. Below are a few of the common Internet access types available in today’s market:
- Fiber Optic Internet – Fiber optic connections use light signals to offer high-speed, reliable and symmetrical upload and download speeds. Enterprise organizations prefer fiber internet because it has low latency, scales easily across multiple distributed locations and handles high bandwidth demands from multiple customers and staff members at one time.
- Fixed Wireless Internet – Fixed wireless internet uses radio signals to deliver high-speed connectivity without relying on physical cables. It can be a viable option for enterprises with locations where wired infrastructure is limited, non-existent or too expensive to deploy. Benefits of fixed wireless include fast installation, increased reliability and simple scalability.
- Broadband Internet – Broadband internet connections are links like cable, digital subscriber lines (DSL) and 4G/5G. Usually, broadband isn’t the best option for enterprises because they’re often shared connections (like cable) or low bandwidth (like DSL and wireless). However, Software-Defined Wide-Area Network (SD-WAN) solutions can optimize broadband networks for enterprise operations by prioritizing mission-critical network traffic and enabling redundancy between multiple internet connections in automatic failover.
- Satellite Internet – Satellite internet works best for enterprise sites in remote or rural areas where physical connections are limited, non-existent or impossible to deploy. Satellite provides coverage across many geographic regions but often has higher latency and limited bandwidth than other connectivity options. For these reasons, satellite is primarily used when no other viable alternatives are available.
- Hybrid Solutions – A combination of internet connections may be the best-fit option for enterprises that need redundancy or diverse connectivity options. For example, combining fiber optic and wireless connections with SD-WAN can offer high-speed and backup connectivity so there’s no downtime.
Factors that Impact Costs for Internet Connections
Internet connections range widely in price due to:
- Varying connection delivery methods (such as the ones listed above)
- Whether it’s a shared or dedicated connection
- Whether an SLA is included with the service
- Whether there are multiple internet circuits deployed for redundancy
- Whether SD-WAN, SD-Internet or other services are deployed over-the-top of the primary connections
- Whether the locations are in rural areas resulting in potential construction or in an easily accessible metro area
- Any customer requirements that need to be completed before accepting the service
- A variety of other factors too numerous to list here

Why Choose DIA Over Shared Internet?
A DIA connection provides enterprise business customers with key advantages of shared Internet connections, including:
- Guaranteed Bandwidth – When an enterprise purchases 1Gbps of bandwidth, they always have access to that 1Gbps of bandwidth for themselves and it’s not shared with other business customers.
- Improved Collaboration & Performance – Today’s technology, like VoIP phone systems, cloud applications, videoconferencing, video streaming applications and remote desktop or desktop as a service (DaaS) applications will perform better due to lower latency and jitter when compared to a shared connection.
- Synchronous Upload & Download Speeds – DIA offers symmetrical upload and download speeds, which is vital for businesses with remote users, VoIP calling and cloud applications. Shared Internet access upload speeds are typically slower than download speeds and are asymmetrical.
Dedicated Internet Access vs. Broadband
DIA outperforms broadband connections by nearly every metric — dedicated connections are faster, easier to scale, higher quality and more reliable. Let’s take a closer look at how these two internet services compare on a variety of factors:
Speed and Performance
Both DIA and broadband offer high-speed connections, but DIA internet speeds are typically faster. Moreover, broadband connections are asymmetrical, so downloads are faster than uploads, which isn’t ideal for modern businesses that rely on multimedia communications. A dedicated fiber internet line offers symmetrical uploading and downloading, improving connectivity for cloud-based applications, VoIP, video conferencing, text, chat and unified communications software. Moreover, dedicated internet service is especially effective for medium-sized and enterprise business networks with multiple locations.
Additionally, there are no hidden “gotcha’s” with dedicated internet as there may be with broadband. Many broadband service providers advertise a misleading maximum speed that’s technically achievable when traffic is low but not when shared among multiple customers. With DIA, there’s no fluctuation in speed. You get the speed you signed up for consistently — and if you don’t, there’s a network problem that your internet service provider (ISP) must fix.

Reliability
Ninety-nine percent uptime isn’t good enough anymore. Modern businesses depend on their internet connections for regular operations to run — and they can’t afford to accommodate frequent, costly network disruptions. DIA is the only option for high uptime.
However, not all providers offer the same service level agreements (SLAs). APX Net’s DIA service relies on Type 1 circuits to deliver an uptime guarantee of 99.999 percent, which, according to the SLA Uptime Calculator, averages less than a second a day or barely five minutes a year of downtime. For all practical purposes, it means no network outages.
Type I vs. Type II circuits
Many broadband providers – and even DIA providers, for that matter – leverage Type II circuits that use more than one network provider to move data packets. Type II circuits create gaps in your network architecture and open opportunities for failure. Additionally, identifying and troubleshooting network problems becomes difficult because providers often point fingers at each other rather than take responsibility.
On the other hand, a dedicated internet provider like APX Net provisions Type I circuits to ensure high-quality, low-latency connectivity. There’s no crossover in connection, no slowdowns and no finger-pointing — there’s only one provider to take responsibility. In addition, Type I DIA providers typically complete repairs within hours, compared to days with broadband and Type II DIA providers offering only “best efforts” service call responses.
Cost
DIA is a powerful business internet connection but typically costs more than broadband to install and manage. Additionally, Type I fiber DIA connections offer higher quality and may be more expensive. If no fiber is available at the location, then a custom build will incur additional fees.
Despite its higher upfront cost, many businesses invest in DIA to avoid long-term costs associated with unexpected network outages and business disruption, which can result in lost sales, revenue, customers and reputational damage.
Quality of Service (QoS)
Service level agreements (SLAs) are a massive draw to developing a relationship with a dedicated business internet service provider. SLAs offer assurances on bandwidth speed, low latency, uptime and other factors that ensure maximum quality and minimum disruptions.
A strong SLA from a Type I DIA provider can help you and your teams sleep at night without worrying about unforeseen downtime. Your IT team can focus on planning and staffing high-value projects, rather than troubleshooting unreliable business internet.

DIA vs. Broadband for Hybrid Work Environments
Remote work is here to stay and most companies allow large swaths of their workforces to continue to work from home at least some of the time. Some will operate office-free, but most will seek to capture the best of both (office and remote) worlds through a combination of work-from-office and work-from-home (or work-from-anywhere) scheduling.
This hybrid model employs broadband connections from employee homes. But, what about the office?
Here, DIA delivers distinct advantages, including:
- Hybrid Work Connection Redundancy: You know how all those Unified Communications (UC) apps advertise the ability to help you keep your operations running during office outages by virtue of sending your employees home, where they can work from their remote connections? The same principle applies in reverse. In fact, remote employees experience more Internet downtime than employees working from the office. That’s because they rely on broadband connections that are subject to all the challenges we’ve been covering here. Having a reliable DIA connection available at the office when employees experience outages – or even excessively slow connectivity – from broadband providers ensures operational continuity.
- Congestion-Proof Office Workdays: Consider the broadband connection challenges with network congestion we’ve already discussed. When your employees come into the office, they become your business’s source of network congestion. A dedicated Internet access connection ensures maximum productivity from your office no matter how many employees are onsite.
- Onsite Security: Cyberthreats skyrocketed when companies scrambled to enable work-from-home business models and hybrid work environments. Sensitive data and infrastructure are more likely to be housed (or accessible) onsite. Secure DIA connections to that infrastructure should be central to any cybersecurity or cyber resilience strategy.
Dedicated Internet Access Pricing
DIA is generally more expensive than broadband if you’re looking solely at connection costs. However, when you factor in security, the impact of reliable speeds on productivity, and higher support levels and uptime, SLA-backed DIA delivers reliable return on investment (ROI) and peace of mind.
Last Considerations Before Choosing Dedicated Internet Access
A couple of final key factors to consider before purchasing a dedicated Internet access connection is whether your business needs SD-WAN and additional connections for network redundancy.
Does Your Business Need SD-WAN?
SD-WAN or software-defined wide area networking leverages widely available Internet connections and works equally well when integrated with an existing MPLS network or as its replacement.
SD-WAN allows your organization to use the public Internet or your private WAN (wide area network), or both, to manage your network traffic. It provides network redundancy and security and centralizes network management for IT teams.
Compared to a traditional WAN deployment, SD-WAN enables businesses to deploy their WANs 100 times faster with three times the cost-savings.
SD-WAN is also typically used for enterprises with multiple locations to assist in connecting geographically disparate branch offices together. You can learn more in our blog, “Multilocation Businesses: How to Connect Multiple Offices Intelligently”.
You can learn more about SD-WAN and if it’s right for you in our blog, “What is SD-WAN? And How Can it Benefit You?”.
Does Your Business Need Additional Connections for Network Redundancy?
Business Internet connections can fail for a variety of reasons from an issue with a last-mile provider to natural disasters to overloaded networks and everything in between. Backup Internet connections and Internet failover solutions are critical to protecting enterprises and small businesses alike from service interruptions.
Internet failover allows your network to “fail-over” to a secondary, backup connection in the event the primary connection is disrupted. Your business may need to consider deploying a secondary connection, such as a fixed wireless Internet access solution to backup your fiber connection.
You can learn more about Internet failover solutions in our blog, “Everything You Need to Know About Internet Failover for Businesses”.
Ready to Try Dedicated Internet Access Built for Business?
Contact an APX Net Data Networks Specialist today!



